
These elements are not generally considered as part of any group. The f-block is in the center-left of a 32-column periodic table but in the footnoted appendage of 18-column tables. The f-block elements,found in the two rows at the bottom of the periodic table, are called inner transition metalsand have valence electrons in the f-orbital's. The f-Block elements (Inner Transition Elements)
#S periodic table series#
The general electronic configuration of D block elements These series of the transition elements are shown in Table 8.1. The transition elements are also known as the d-block elements, because while the outermost level contains at most two electrons, their next to outermost main levels have incompletely filled d sub-orbitals, which are filled-up progressively on going across the periodic table from 8to 18 electrons. The d-block elements are called transition metalsand have valence electrons in d orbital's. The d-Block elements (Transition Elements) All of the elements that are commonly recognized as metalloids are in the p-block: boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antinomy, and tellurium. Metalloids have properties of both metals and nonmetals, but the term 'metalloid' lacks a strict definition. Their valence shell electronic configuration is ns2 np1-6(except for He). Boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine and helium head the groups.
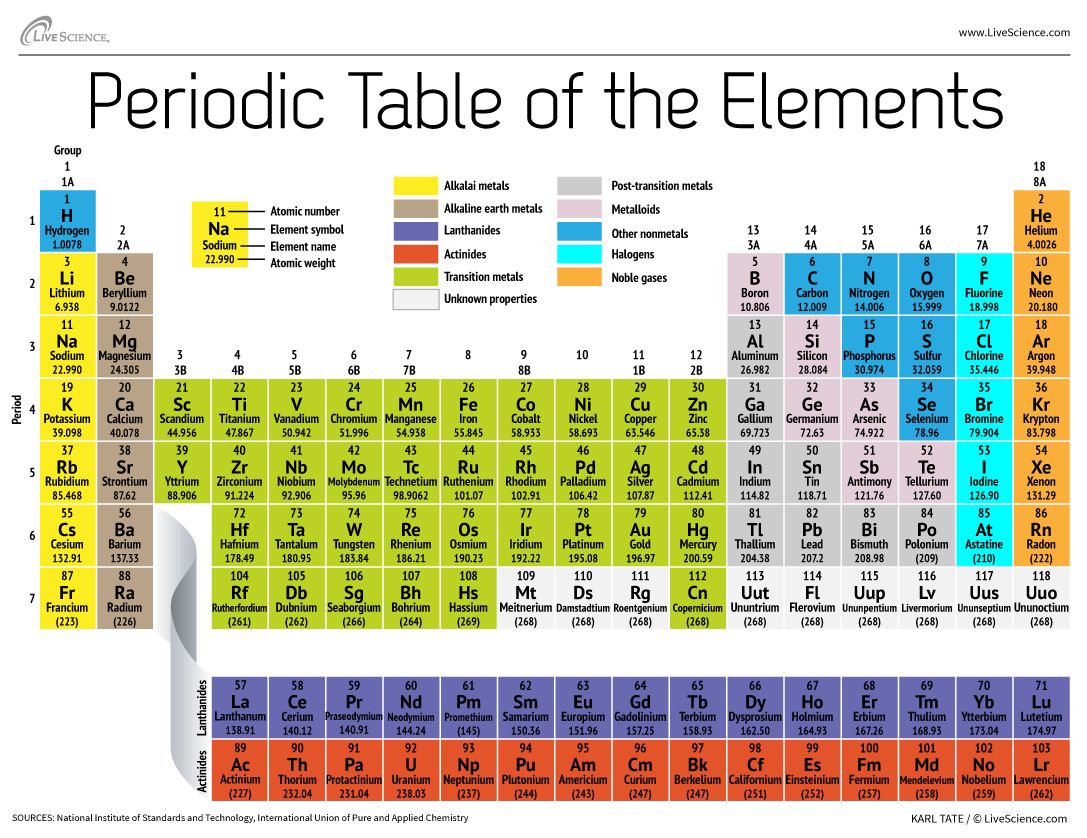
Consequently there are six groups of p–block elements in the periodic table numbering from 13 to 18. In p-block elements the last electron enters the outermost p orbital. The general electronic configuration of P block elements This group is nonreactive and generally does not bond with other elements, preferring to exist by themselves. The group that resides in column 8A is called the noble gases.
#S periodic table full#
The noble gases have full p-orbital's and are nonreactive. They include the boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and flourine families in addition to the noble gases. The p-block elements are found on the right side of the periodic table. The p-block elements are a very diverse group of elements with a wide range of properties.

There are 35 p-block elements, all of which have valence electrons in the p orbital. The p-block is the area of the periodic table containing columns 3A to column 8A (columns 13-18), not including helium. These are so called because they form hydroxides on reaction with water which are strongly alkaline in nature.

They are collectively known as the alkali metals. Group 1 of the Periodic Table consists of the elements: lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, caesium and francium. Why is potassium considered as an S block element? The elements in group two are called the alkaline earth metals. The elements in group one are called the alkali metals. Elements in these are in the first two periodic table groups. The electron in their most outward electron shell are in the s-orbital.

Group 2 is the alkali earth metals which have two valence electrons, filling their s sublevel. They have low ionization energies which makes them very reactive. Group 1 are the alkali metals which have one valence electron. S-block elements are the elements found in Group 1 and Group 2 on the periodic table. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital thus, the blocks are: The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet.The respective highest-energy electrons in each element in a block belong to the same atomic orbital type. A block of the periodic table of elements is a set of adjacent groups.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
